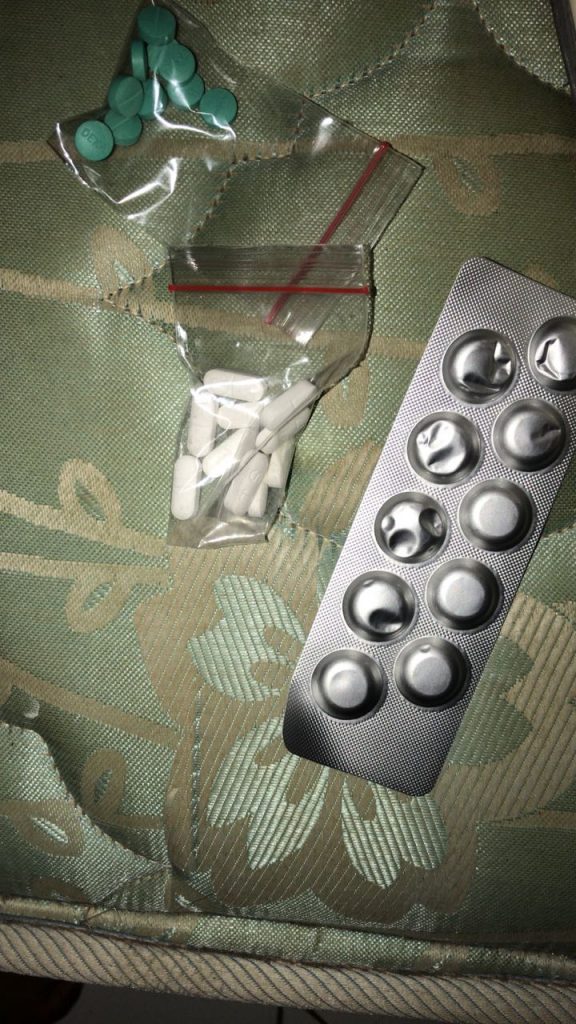
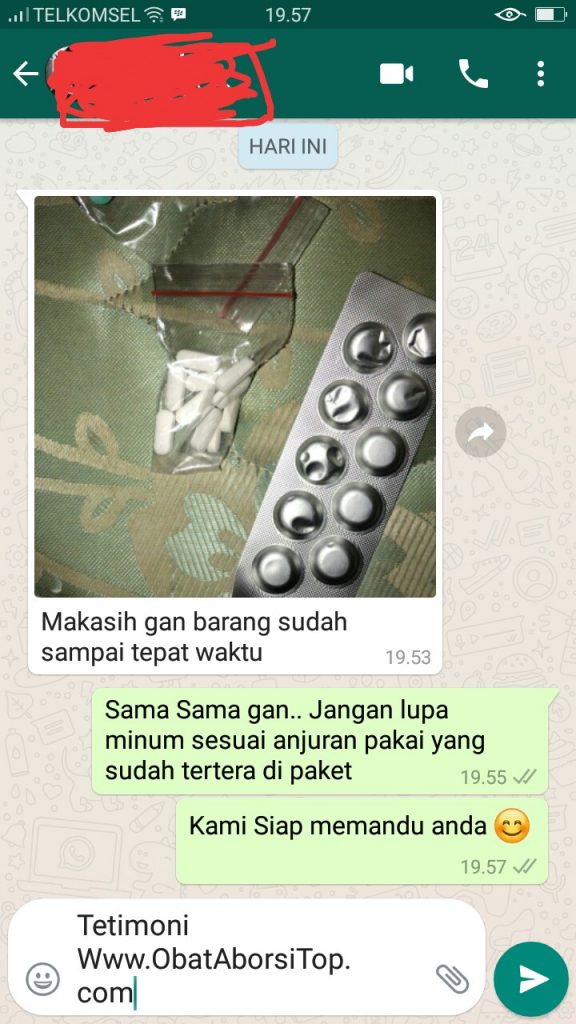
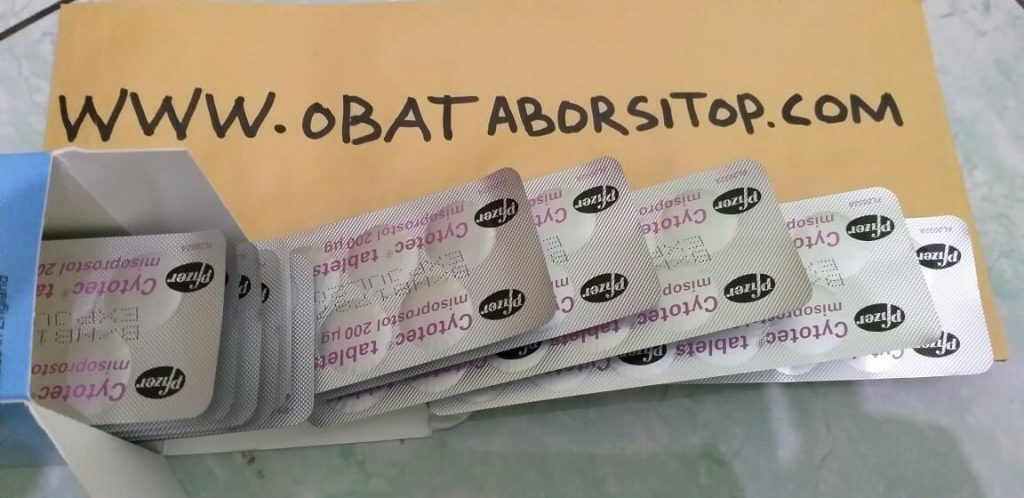
Testimoni Pelanggan
ObatAborsiTop.com merupakan platform jual obat aborsi asli secara online dengan kualitas terbaik. Obat aborsi kami bergaransi 100 % uang kembali dan ASLI disertai dengan konsultasi gratis. Obat aborsi kami sangat cocok untuk usia kandungan 1, 2, 3 , 4 bulan.
TENTANG KAMI
Jual Obat Aborsi Cytotec Penggugur Kandungan Asli - Solusi Terbaik Menggugurkan Kandungan
Cara paling aman dan efektif untuk menggugurkan kandungan adalah dengan mengkonsumsi obat aborsi cytotec penggugur kandungan yang telah terpercaya dan ampuh untuk mengugurkan kandungan. Ya, untuk itu bagi Anda yang ingin menggugurkan kandungan secara cepat dan tepat, ada baiknya Anda mencari apotek atau tempat yang jual obat aborsi dan mendapatkan jual obat aborsi cytotec atau sejenisnya yang bisa menggugurkan kandungan secara aman. Jika Anda sedang dalam pencarian tersebut dan membutuhkan obat untuk menggugurkan kandungan, artinya Anda telah berada di tempat yang tepat. Karena disini Anda bisa temukan obat terbaik yang bisa membuat kandungan Anda gugur secara aman.
Kami menyediakan solusi dan cara menggugurkan kandungan secara aman bagi siapa saja yang berkeinginan untuk menggugurkan kandungan secara mudah dan cepat. Obat terlambat datang bulan yang kami sediakan bukan sembarang obat karena obat yang tersedia disini merupakan obat aborsi aman yang terbukti terpercaya serta ampuh digunakan untuk berbagai kalangan yang ingin mengaborsi kandungannya. Kami menawarkan sebuah obat telah haid yang memiliki khasiat nyata yang tidak akan membuat Anda kecewa dengan hasil yang diberikan. Selain itu, obat ini juga memiliki nilai guna yang luar biasa dalam hal menggugurkan kandungan. Anda bukan hanya bisa menggugurkan kandungan Anda dengan kemungkinan yang besar namun juga tetap aman dan mudah.
Jika Anda tertarik dengan obat yang kami tawarkan, kami juga menawarkan harga obat aborsi yang sangat murah dan terjangkau. Anda tak perlu khawatir mengeluarkan banyak uang untuk aborsi Anda karena kami menawarkan sebuah solusi aborsi yang hemat dan murah tanpa efek samping berbahaya. Selain itu, obat aborsi murah ini juga ditawarkan dengan sebuah garansi menarik dan menjanjikan yaitu 100% money-back guarantee yang menunjukan bahwa obat ini memang aman dan kami berani menjaminnya dengan sebuah garansi yang tinggi. Saking amannya, Anda bisa menggunakan obat telat bulan ini lebih dari 1 kali seumur hidup. Bagaimana? Cukup menjanjikan bukan?
Selain menawarkan sebuah obat aborsi bergaransi dan juga murah, kami juga menawarkan konsultasi gratis bagi siapa saja yang ingin mendapatkan obat aborsi dari tempat kami. Anda bisa datang ke website kami lalu konsultasikan segera kepada kami apa yang menjadi keluhan dan masalah Anda. Kami akan dengan senang hati membantu masalah Anda berkaitan dengan aborsi atau pengguguran kandungan. Jadi, Anda bukan hanya bisa mendapatkan obat aborsi terbaik tapi juga include sebuah konsultasi untuk menggugurkan kandungan. Datang dan temukan sendiri perbedaan kami dengan penyedia obat aborsi lainnya. Kami benar-benar menyediakan best seller obat aborsi yang merupakan terobosan dunia farmasi terbaru.
Sekarang, Anda tidak lagi perlu risau jika ingin menggugurkan kandungan Anda karena kami memiliki solusi terbaik dan terbaru untuk Anda yang ingin menggugurkan kandungan dengan mudah. No 1 obat aborsi yang kami tawarkan ini benar-benar tepat guna dan bukan sebuah rahasia lagi bahwa obat ini memang sangat mudah untuk dipakai menggugurkan kandungan. Disebabkan oleh keamanannya dan juga khasiatnya. Selain bisa mendapatkan obat dengan harga murah, konsultasi ekslusif yang kami berikan tentu sangat membantu Anda. Jadi, Anda tak perlu ragu atau gengsi dan langsung saja pesan sekarang sebelum terlambat. Dan jangan lupa juga untuk hubungi kami sekarang juga untuk informasi lebih lanjut mengenai obat aborsi dan solusi terbaik menggugurkan kandungan.
Kami menyediakan solusi dan cara menggugurkan kandungan secara aman bagi siapa saja yang berkeinginan untuk menggugurkan kandungan secara mudah dan cepat. Obat terlambat datang bulan yang kami sediakan bukan sembarang obat karena obat yang tersedia disini merupakan obat aborsi aman yang terbukti terpercaya serta ampuh digunakan untuk berbagai kalangan yang ingin mengaborsi kandungannya. Kami menawarkan sebuah obat telah haid yang memiliki khasiat nyata yang tidak akan membuat Anda kecewa dengan hasil yang diberikan. Selain itu, obat ini juga memiliki nilai guna yang luar biasa dalam hal menggugurkan kandungan. Anda bukan hanya bisa menggugurkan kandungan Anda dengan kemungkinan yang besar namun juga tetap aman dan mudah.
Jika Anda tertarik dengan obat yang kami tawarkan, kami juga menawarkan harga obat aborsi yang sangat murah dan terjangkau. Anda tak perlu khawatir mengeluarkan banyak uang untuk aborsi Anda karena kami menawarkan sebuah solusi aborsi yang hemat dan murah tanpa efek samping berbahaya. Selain itu, obat aborsi murah ini juga ditawarkan dengan sebuah garansi menarik dan menjanjikan yaitu 100% money-back guarantee yang menunjukan bahwa obat ini memang aman dan kami berani menjaminnya dengan sebuah garansi yang tinggi. Saking amannya, Anda bisa menggunakan obat telat bulan ini lebih dari 1 kali seumur hidup. Bagaimana? Cukup menjanjikan bukan?
Selain menawarkan sebuah obat aborsi bergaransi dan juga murah, kami juga menawarkan konsultasi gratis bagi siapa saja yang ingin mendapatkan obat aborsi dari tempat kami. Anda bisa datang ke website kami lalu konsultasikan segera kepada kami apa yang menjadi keluhan dan masalah Anda. Kami akan dengan senang hati membantu masalah Anda berkaitan dengan aborsi atau pengguguran kandungan. Jadi, Anda bukan hanya bisa mendapatkan obat aborsi terbaik tapi juga include sebuah konsultasi untuk menggugurkan kandungan. Datang dan temukan sendiri perbedaan kami dengan penyedia obat aborsi lainnya. Kami benar-benar menyediakan best seller obat aborsi yang merupakan terobosan dunia farmasi terbaru.
Sekarang, Anda tidak lagi perlu risau jika ingin menggugurkan kandungan Anda karena kami memiliki solusi terbaik dan terbaru untuk Anda yang ingin menggugurkan kandungan dengan mudah. No 1 obat aborsi yang kami tawarkan ini benar-benar tepat guna dan bukan sebuah rahasia lagi bahwa obat ini memang sangat mudah untuk dipakai menggugurkan kandungan. Disebabkan oleh keamanannya dan juga khasiatnya. Selain bisa mendapatkan obat dengan harga murah, konsultasi ekslusif yang kami berikan tentu sangat membantu Anda. Jadi, Anda tak perlu ragu atau gengsi dan langsung saja pesan sekarang sebelum terlambat. Dan jangan lupa juga untuk hubungi kami sekarang juga untuk informasi lebih lanjut mengenai obat aborsi dan solusi terbaik menggugurkan kandungan.